Understanding General Concepts¶
Getting started¶
One you start using OpenEduCat Studio, you automatically create a new module that contains all your modifications. These modifications can be done on existing screens (views), by adding new fields in existing applications, or by creating an entirely new model.
What is a Module?¶

What is a Model (also called Object)?¶
A Model determines the logical structure of a database and fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized, and manipulated. In other words, a model is a table of information that can be bridged with other tables.
What are Fields?¶
Relational Fields in detail¶
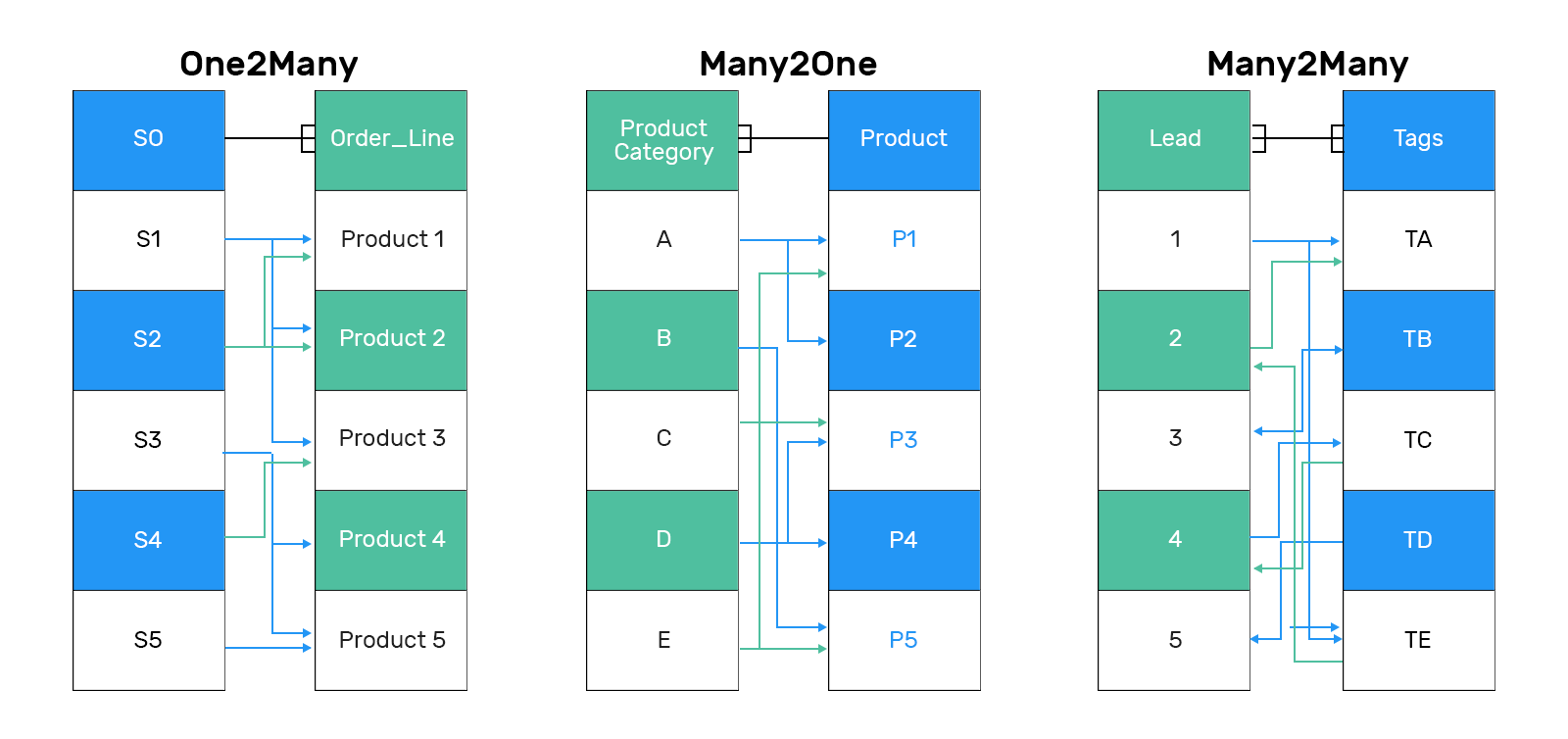
Note
An One2many field must have a Many2one related to it.
What are Views?¶
Views define how records are displayed. They are specified in XML which means that they can be edited independently from the models that they represent. There are various types of views in OpenEduCat, and each of them represents a mode of visualization. Some examples are: form, list, kanban.